George Soros Finances Group Helping Facebook Flag ‘Disputed’ Stories
The organization partnered with Facebook to help determine whether a certain story is “disputed” is financed by billionaire George Soros and a slew of other left-wing funders.

The “International Fact-Checking Network (IFCN)” drafted a code of five principles for news websites to accept, and Facebook yesterday announced it will work with “third-party fact checking organizations” that are signatories to the code of principles.
Facebook says that if the “fact checking organizations” determine that a certain story is fake, it will get flagged as disputed and, according to the Facebook announcement, “there will be a link to the corresponding article explaining why. Stories that have been disputed may also appear lower in News Feed.”
IFCN is hosted by the Poynter Institute for Media Studies. A cursory search of the Poynter Institute website finds that Poynter’s IFCN is openly funded by Soros’ Open Society Foundations as well as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Google, and the National Endowment for Democracy.
Poynter’s IFCN is also funded by the Omidyar Network, which is the nonprofit for liberal billionaire eBay founder Pierre Omidyar. The Omidyar Network has partnered with the Open Society on numerous projects and it has given grants to third parties using the Soros-funded Tides Foundation. Tides is one of the largest donors to left-wing causes in the U.S.
Another significant Poynter Institute donor is the Craig Newmark Foundation, the charitable organization established by Craigslist Founder Craig Newmark. On Monday, just days before the announcement of the Facebook partnership, Poynter issued a press release revealing that Newmark donated $1 million to the group to fund a faculty chair in journalism ethics.
States the press release:
The gift will support a five-year program at Poynter that focuses on verification, fact-checking and accountability in journalism. It’s the largest donation Poynter’s ever received from an individual foundation.
The Newmark Chair will expand on Poynter’s teaching in journalism ethics and develop certification programs for journalists that commit to ethical decision-making practices. The faculty member will also organize an annual conference on ethics issues at Poynter and be a regular contributor to Poynter.org.
Newmark funds scores of liberal groups also financed by Soros, including the Sierra Club, the New America Foundation, and the Sunlight Foundation.
Newmark also finances the investigative journalism group called the Center for Public Integrity, where he serves on the board. Soros’ Open Society is another Public Integrity donor.
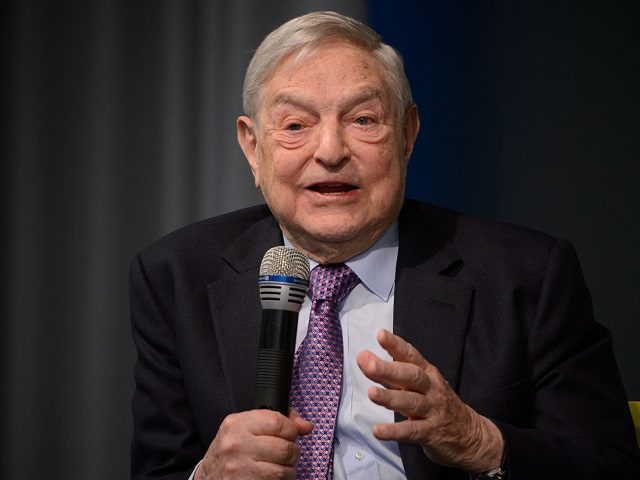
Soros has earned his megafortune in part by short selling currencies and causing economic crises. He is credited with breaking the pound on September 16, 1992 in a day that became known in Britain as “Black Wednesday.” He reportedly made $1.2 billion from that crisis. In 2002, he was convicted for insider trading.
Poynter, meanwhile, has hosted controversial journalism programs in the past, including one that was accused of downplaying the threat of global Islamic terrorism. FoxNews.com reported the course suggested reporters “keep the death toll from Islamic terrorism in ‘context’ by comparing that toll to the number of people killed every year by malaria, HIV/AIDS and other factors.”
The course taught reporters that the term “jihad” means internal struggle, and it discussed what it claimed was the issue of “right-wing activists” attempting to link American Muslims to terrorism.
Continued:
The section includes the good-journalism tip that reporters should check to see if experts they’re interviewing “have a bias or a stake in the story you are covering.” But then it only cites examples of anti-Muslim groups.
The course in Islam, Fox News reported, was supported by a group calling itself the Social Science Research Council, which has received funding from Soros-financed groups.
In response to the report, the Poynter Institute explained that it created the course “as a tool for journalists who want to be accurate in educating their audience about the religion and culture of Islam, Muslim communities in the U.S., and the distinctions between Islam as a political movement and the radical philosophies that inspire militant Islamists.”
“We believe there is a need to better understand the complexities of Muslim societies and the online course offered by Poynter and Washington State University is a vital resource toward that end,” Poynter added.
“The values underpinning the course are truth, accuracy, independence, fairness, minimizing harm and context — the core journalistic values on which we build all our teaching here at Poynter.”
Poynter’s IFCN code of principles for news outlets, meanwhile, reads as follows:
1. A COMMITMENT TO NONPARTISANSHIP AND FAIRNESS
We fact-check claims using the same standard for every fact check. We do not concentrate our fact-checking on any one side. We follow the same process for every fact check and let the evidence dictate our conclusions. We do not advocate or take policy positions on the issues we fact-check.
2. A COMMITMENT TO TRANSPARENCY OF SOURCES
We want our readers to be able to verify our findings themselves. We provide all sources in enough detail that readers can replicate our work, except in cases where a source’s personal security could be compromised. In such cases, we provide as much detail as possible.
3. A COMMITMENT TO TRANSPARENCY OF FUNDING & ORGANIZATION
We are transparent about our funding sources. If we accept funding from other organizations, we ensure that funders have no influence over the conclusions we reach in our reports. We detail the professional background of all key figures in our organization and explain our organizational structure and legal status. We clearly indicate a way for readers to communicate with us.
4. A COMMITMENT TO TRANSPARENCY OF METHODOLOGY
We explain the methodology we use to select, research, write, edit, publish and correct our fact checks. We encourage readers to send us claims to fact-check and are transparent on why and how we fact-check.
5. A COMMITMENT TO OPEN AND HONEST CORRECTIONS
We publish our corrections policy and follow it scrupulously. We correct clearly and transparently in line with our corrections policy, seeking so far as possible to ensure that readers see the corrected version.
Aaron Klein is a New York Times bestselling author and hosts the popular weekend talk radio program, “Aaron Klein Investigative Radio.” Follow him on Twitter @AaronKleinShow. Follow him on Facebook.
With research by Joshua Klein and Brenda J. Elliott.
Source: Soros Finances Group Helping Facebook Flag ‘Disputed’ Stories